The Best Car Insurance Companies for 2026
The best auto insurance companies are able to provide proper coverage and great perks at low rates while also delivering excellent customer service when accidents happen, and claims have to be filed.
Find out which car insurers are ranked among the best when it comes to the top overall customer experience — ensuring coverage for you, your passengers, and everyone else on the road.
Rankings for the best auto insurance companies were identified in partnership with Insure.com, which analyzed the 20 leading issuers of auto insurance and surveyed more than 3,700 auto insurance customers.
Each company was rated based on price, customer service, website, mobile app, and customer recommendation while also considering the ratings of A.M. Best. (A.M. Best financial ratings are assessments of the insurer’s financial health and ability to fulfill their financial obligations, especially claims, to policyholders.)
1. AAA (The Auto Club Group): Best for Trustworthy Service
AAA is one of the most reputable car insurance companies that often garners rave reviews regarding their excellent and professional customer service.
As part of auto insurance policies, AAA Accident Assist is a handy benefit when you need roadside assistance, and it guarantees repairs for the life of the vehicle when using an AAA-affiliated repair shop.
You must be an AAA member to be eligible for the company’s auto insurance, and coverage varies by state.
AAA Auto Insurance Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Read our review of AAA insurance offerings.
2. CSAA Insurance Group: Best for Available Discounts
CSAA Insurance Group is is a part of AAA, so you’ll need AAA membership. But, you are eligible for a wide range of coverages, programs, and potential discounts, such as roadside assistance and discounts at AAA-partnered locations, in addition to top-tier customer service.
CSAA Auto Insurance Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Read our review of CSAA Insurance coverages and ratings.
3. USAA: Best for Military Members & Families
USAA is one of the country’s largest financial institutions and offers auto insurance policies (and other financial products and services) only to active U.S. military service members, veterans, and their families.
You can get discounts when your car is parked in the garage on base. You could get a waiver of your collision deductible if an accident wasn’t your fault. Policy renewals are also quite lenient, even if you have claims on record.
USAA Auto Insurance Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Read our USAA insurance review.
4. Auto Club of Southern California: Best for Helpful Tools & Resources
The Auto Club of Southern California is part of AAA but operates separately and provides auto insurance in 20 states — not just for residents of Southern California.
The insurer is often noted for its stellar resources, such as easy-to-use websites, mobile apps, local branches, car-buying guides, travel-planning tools, and more.
Auto Club of South California Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Read our Automobile Club of Southern California insurance review.
5. Erie Insurance: Best for Customer Service
Erie Insurance is often heralded for having knowledgeable and pleasant customer service agents.
The insurer offers pet protection, locksmith services, rental reimbursement coverage, and no-deductible windshield repairs as part of their policies. Accident forgiveness becomes available after three years of coverage with Erie Insurance.
Erie Insurance serves only 12 states–mostly in the Northeast.
Erie Auto Insurance Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Read our review on Erie Insurance.
What are the Different Types of Car Insurance Coverage?
Most U.S. states (except New Hampshire) have minimum requirements for auto insurance coverage.
Full coverage
When you have “full coverage,” it often means that you have liability, collision, and comprehensive coverages (further detailed below).
Liability-only
Liability insurance coverage is meant to pay other parties for damage caused by your vehicle.
In nearly all states, this is the bare minimum level of auto insurance required.
Bodily injury liability
This coverage will pay for medical expenses, legal fees, loss of wages and other costs associated with injuries and death in accidents where your vehicle was in motion — whether or not you were driving it.
Property damage liability
This coverage will pay others for damage to another vehicle and property caused while your vehicle was in motion — whether or not you were driving it.
Depending on your state laws, additional coverage may be required. Your auto loan provider may as require these coverages:
Medical payments or personal injury protection (PIP)
Medical payments coverage pays for medical expenses for you and your passengers (even if you’re driving someone else’s vehicle) after an accident, regardless of who is at fault.
PIP covers medical expenses, lost wages, funeral costs and other expenses for you and your passengers after an accident.
Uninsured motorist coverage
This coverage will pay for bodily injury and, in some states, property damage to you and other passengers in your vehicle from an accident where the at-fault party does not have (or does not have sufficient) coverage.
Optional Insurance Coverage
For the most part, the state-required minimum auto insurance coverage is focused on compensating other parties in accidents that result from your vehicle.
However, accidents and other types of incidents can also cause extensive damage to your car, which is where collision and comprehensive coverage can be useful.
Both types of additional coverages are not required by any U.S. state, but lenders may require them as long as you still have an outstanding loan for your vehicle. (You can remove them from your policy after paying off the loan.)
Collision
Collision coverage insures you against damage to your vehicle caused by a collision with another vehicle or object (e.g., parked vehicles, trees, and fences) when you are the at-fault party.
This coverage applies only to damages sustained to your car while it is in motion.
Comprehensive
Comprehensive coverage covers hazards while your vehicle is parked and not in motion.
Common examples of such damages include those caused by falling trees, vandalism, storms, fire, and more.
The best part is that your car insurance premiums won’t increase as a result of a claim because you’re typically not at fault for these incidents.
What Factors Affect Your Car Insurance Rates?
Car insurance companies use a ton of data to determine your risk of accidents and the likelihood of claims.
These are often the factors considered as part of their underwriting process:
Coverage
If you want more coverage, you’re going to pay more for it. So, for example, full coverage is going to cost significantly more than just liability-only coverage.
Remember that you may have to pay for additional coverage depending on state requirements.
Gender and age
Gender and age are used to generalize the driver and to judge their risk of getting into more accidents.
Not surprisingly, young male drivers are often considered very risky and tend to pay higher car insurance premiums.
See car insurance rates for younger drivers:
- Car insurance for 16-year-olds
- Car insurance for 17-year-olds
- Car insurance for 18-year-olds
- Car insurance for 19-year-olds
Marital status
Married couples have been found to be in fewer accidents and file fewer claims.
Additionally, married drivers are often eligible for lower premiums through multi-vehicle discounts and bundling auto insurance with other types of insurance.
Driving experience and history
Those who have been driving longer and those who have few or minor violations and accidents over a long period of time are seen as less risky drivers.
Credit score
The research found that people with lower credit scores are more likely to file claims and insurers may use this information to calculate premiums.
So, a higher credit score could play in your favor when it comes to calculating premiums.
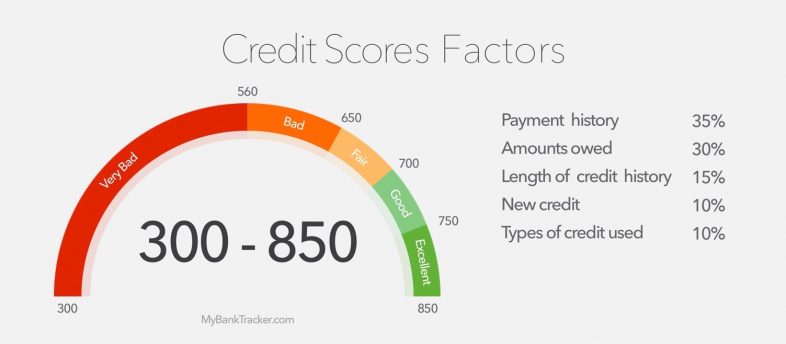
These states forbid insurers from using consumer credit histories when underwriting auto insurance policies:
- California
- Hawaii
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
Location
Location not only helps to identify the required coverages for the state, but insurance companies also use your location to look at historical data to estimate the likelihood of natural disasters, crime, frequency of accidents, and other risks associated with your area.
Insurance history
Auto insurers find that drivers who’ve had uninterrupted coverage are less likely to get into accidents. So, if you’ve maintained an auto insurance policy continually (without lapsing), you’re more likely to get lower rates.
Claims history
Simply, a history of many claims — whether with the current insurer or previous insurers — will likely result in higher rates or denied coverage. To no surprise, this is especially the case for larger claims where you’re the at-fault party.
Vehicle
The insured vehicle will be considered for its purchase price, safety features, safety tests, repair costs, and more.
Data may reveal that your vehicle make and/or model is known to be involved in accidents more often or more likely to be targeted for theft and crime.
Purpose of vehicle
You will usually be asked what you use the car for, such as commuting to work or school. Or, you’re just driving it occasionally for recreation.
Additionally, if you plan to use the car for commercial purposes (such as ridesharing) or as part of running a business, you’d have to ensure that your vehicle is covered properly because insurers are picky with coverage depending on the use case.
Mileage
Your annual mileage provides the car insurance company with information on how often you drive. The more you drive, the more likely to be part of accidents — so you can expect to pay higher rates. (There are programs for lower rates if you drive very little.)
Average Car Insurance Rates by State
| State | Full coverage | Minimum coverage |
|---|---|---|
| Alabama | $1,713 | $498 |
| Alaska | $1,560 | $412 |
| Arizona | $1,783 | $578 |
| Arkansas | $1,763 | $449 |
| California | $2,125 | $606 |
| Colorado | $1,948 | $553 |
| Connecticut | $2,036 | $891 |
| DC | $2,188 | $839 |
| Delaware | $1,921 | $843 |
| Florida | $2,162 | $828 |
| Georgia | $1,865 | $684 |
| Hawaii | $1,589 | $485 |
| Idaho | $1,285 | $377 |
| Illinois | $1,538 | $493 |
| Indiana | $1,266 | $430 |
| Iowa | $1,352 | $326 |
| Kansas | $1,689 | $464 |
| Kentucky | $2,368 | $669 |
| Louisiana | $2,601 | $771 |
| Maine | $1,080 | $355 |
| Maryland | $1,816 | $853 |
| Massachusetts | $1,466 | $520 |
| Michigan | $3,141 | $1,855 |
| Minnesota | $1,619 | $614 |
| Mississippi | $1,684 | $413 |
| Missouri | $1,798 | $546 |
| Montana | $1,963 | $447 |
| Nebraska | $1,500 | $393 |
| Nevada | $2,402 | $717 |
| New Hampshire | $1,086 | $424 |
| New Jersey | $1,993 | $846 |
| New Mexico | $1,604 | $479 |
| New York | $2,062 | $867 |
| North Carolina | $1,425 | $438 |
| North Dakota | $1,577 | $423 |
| Ohio | $1,191 | $406 |
| Oklahoma | $1,815 | $418 |
| Oregon | $1,496 | $674 |
| Pennsylvania | $1,700 | $502 |
| Rhode Island | $2,040 | $738 |
| South Carolina | $1,653 | $617 |
| South Dakota | $1,643 | $323 |
| Tennessee | $1,493 | $462 |
| Texas | $1,823 | $538 |
| Utah | $1,492 | $565 |
| Vermont | $1,410 | $398 |
| Virginia | $1,196 | $380 |
| Washington | $1,620 | $537 |
| West Virginia | $1,654 | $541 |
| Wisconsin | $1,335 | $401 |
| Wyoming | $1,782 | $328 |
Low premiums might be nice if you are trying to save money, but you don’t want to have a bad experience when it’s time to file a claim. Here are some other insurance features to check out to ensure you are getting the best insurance coverage for your needs.
Premiums
The premium is the price you pay for your auto insurance policy. You can pay premiums annually, quarterly, or monthly. Typically, when you pay more upfront, your insurer will give you more of a discount.
Discounts
Auto insurers will offer many discounts to help keep your premiums low.
Here are some examples of discounts you may be eligible for depending on the insurer and your state of residency:
- Safety equipment like anti-theft, anti-lock brakes, etc.
- Multi-policy discount
- Good driver discount
- Paperless billing
- Good student billing
- Defensive driving discount
Deductibles
The deductible is the amount you are responsible for in case of a claim. In some cases, you may have different deductibles for different types of damages, even if it occurs in the same incident. Most often, the lower your deductible, the higher your monthly premium.
However, if you choose to pay a higher premium, you may opt for a lower monthly premium. If your card is damaged in a covered incident, the insurance company will give a check to you to cover the damage. For instance, if your total claim amount is $3,000 and your deductible is $500, the auto insurance company will give you a check for $2,500.
Financial health and credit risk
When choosing an auto insurer, you want to make sure their financial rating is good. Otherwise, they may not be financially healthy enough to pay your claims. There are a few companies that rate the financial stability of auto insurance companies:
- Moody’s
- Fitch
- Standard & Poor’s
Insurance companies rated as financially stable are more likely to provide you with excellent customer service, and a good insurance product and will pay your claims on time and as agreed.
Customer service
Another important feature of an auto-insurer is their customer service. Often, a great insurance policy at a competitive price can be spoiled by bad or nonresponsive customer service. Ideally, you want a company with 24-hour phone customer service and a robust digital interface, either via web or smartphone app, to access your account.
Filing claims with your smartphone and managing the claims process online can be a huge help. If it’s not easy to access and manage your account online, this is a sign that you may run into problems with your insurer down the road.
Additional perks and benefits
Finally, you should look for the “icing on the cake” when researching your insurance options. Nowadays, insurance companies are offering extra perks and benefits for their customers. Here are some to watch out for:
- Pet insurance
- Accident forgiveness
- Vanishing deductibles
- Zero deductible windshield replacement (available in select states)
- Roadside assistance
Key terms
Appraisal
The appraisal process determines your vehicle’s fair value and the cost of its repairs after a car accident. If the repairs cost more than what the car is worth, your payout will be based on the appraisal’s value.
Deductible
This is the amount you are responsible for paying when a claim is filed. Your deductible will be “deducted” from the total claim amount when you receive an insurance payout.
CLUE report
CLUE stands for the Comprehensive Loss Underwriting Exchange, which is a database that insurance companies consult when you apply for coverage or request a quote. The report generally contains up to seven years of personal-auto and personal-property claims history.
Gap insurance
If your car is considered a total loss and your remaining auto loan exceeds the amount, gap insurance will pay off an auto loan.
No-fault insurance
No-fault means that all parties involved in any incident must submit claims through their own insurance policy instead of recovering from the at-fault party’s insurer. No-fault insurance is the basis for auto insurance laws in 12 U.S. states.
Non-renewal
This is a notice you may get from your car insurance company when they choose not to renew your policy at the end of its term.
SR-22
With this type of insurance, your auto insurer assures your state’s motor vehicle or insurance department that you’ll maintain coverage for a certain period of time. If you don’t, the insurer will alert your state, and your driver’s license could be suspended or revoked. Your insurance company will charge you more for this service, which makes SR-22 insurance more expensive.
Total loss
When the cost to fix your car exceeds the car’s appraised value, your insurance company will total out your car and consider it a total loss. They will not pay to fix it but instead pay the actual cash value (ACV) of the car. If your settlement is less than what you owe, you’re responsible for the balance of your loan.
Read the car insurance guide based on your state
- Arizona
- Florida
- Hawaii
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Maine
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- New Jersey
- North Carolina
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Washington
- Wisconsin
Industry Ratings of the Top U.S. Car Insurance Companies
| Company | A.M. Best Financial Strength Rating | A.M. Best Issuer Credit Rating |
|---|---|---|
| AAA (The Auto Club Group) | A | a |
| CSAA Insurance Group | A | a+ |
| USAA | A++ | aaa |
| Auto Club of Southern California | A | a |
| Erie Insurance | A+ | aa- |
| State Farm | A++ | aa+ |
| GEICO | A++ | aaa |
| Progressive | A+ | aa |
| Allstate | A+ | aa |
| Farmers | A | a |
| Travelers | A++ | aa+ |
| American Family Insurance | A | a+ |
| Nationwide | A+ | aa- |
| Auto Club Exchange | A | a |
| Chubb | A++ | aa+ |
| Kemper | A- | a- |
| Mercury Insurance | A | a+ |
| Amica | A+ | aa- |
| COUNTRY Financial | A+ | aa- |
| The Hanover Insurance Company | A | a+ |





